Unmasking Deceptive Emails: Five Signs an Emails is Too Good to be True
Introduction:
In the age of digital communication, emails has become an integral part of our daily lives. While it is a convenient and efficient means of correspondence, it is crucial to remain vigilant against potential threats posed by deceptive emails. Cybercriminals employ various tactics to lure unsuspecting individuals into their traps, and recognizing the signs of a fraudulent email is essential for safeguarding personal and sensitive information. In this article, we will explore five telltale signs that an email might be too good to be true.
Unusual Sender Information:
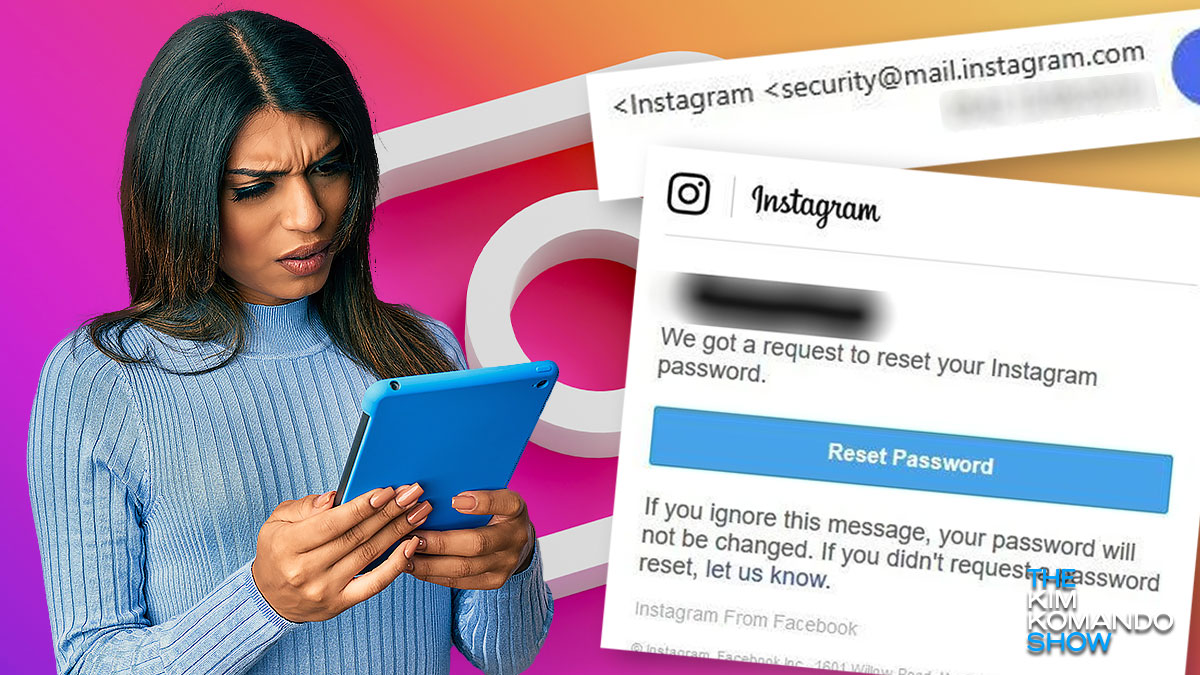
One of the first red flags to watch out for is unusual sender information. Legitimate organizations and businesses usually have professional and consistent email addresses. Be wary of emails that come from suspicious or generic addresses, as well as those that use misspelled versions of well-known company names. Cybercriminals often attempt to mimic official communications by using deceptive sender information to trick recipients.
Unexpected Attachments or Links:
A common tactic employed by phishing emails is the inclusion of unexpected attachments or links. If an email prompts you to download an attachment or click on a link unexpectedly, exercise caution. Legitimate organizations typically inform recipients in advance or provide context for such actions. Cybercriminals may use these attachments or links to install malware on your device or redirect you to fraudulent websites aimed at stealing your personal information.
Urgency and Pressure Tactics:
Another sign that an email might be a scam is the use of urgency and pressure tactics. Cybercriminals often create a sense of urgency to manipulate individuals into taking immediate action without thoroughly considering the consequences. Be skeptical of emails that claim your account will be suspended, funds will be forfeited, or other dire consequences will occur unless you act urgently. Legitimate organizations typically provide clear information and allow users to verify the situation independently.
Grammar and Spelling Errors:
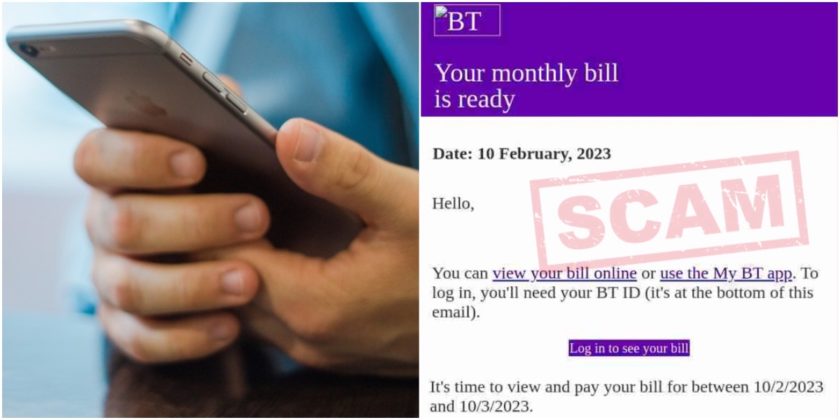
While it may seem basic, the presence of grammar and spelling errors can be a strong indicator of a fraudulent email. Legitimate organizations invest in professional communication, and their emails undergo thorough proofreading. Cybercriminals, on the other hand, may not pay attention to such details, leading to inconsistencies and errors in their messages. If an email contains multiple grammatical mistakes or awkward language, approach it with caution.
Requests for Personal Information:
A crucial red flag signaling a potentially deceptive email is any request for personal or sensitive information. Legitimate organizations typically do not ask for sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details, via email. Cybercriminals may attempt to trick individuals into providing such information by posing as trusted entities. Always verify the legitimacy of such requests independently through official channels before divulging any confidential information.
Generic Greetings or Lack of Personalization:
Legitimate organizations usually personalize their communications, addressing recipients by their names and providing specific details related to the recipient’s account or recent interactions. Beware of emails that use generic greetings such as “Dear Customer” or lack any personalized information. Cybercriminals often send mass phishing emails without personalization, hoping to target a broad audience. If an email fails to address you by name or lacks specific details relevant to your interactions with the sender, exercise caution.
Inconsistent Branding and Logo Usage:

Scammers often attempt to replicate the branding and logos of well-known companies to create a false sense of legitimacy. However, careful scrutiny may reveal inconsistencies in the logo, color schemes, or overall design. Legitimate organizations maintain a consistent brand image across their communications. If you notice any discrepancies or deviations from the usual branding in an email, it’s a potential sign of a fraudulent attempt.
Unusual Email Content:
Pay attention to the overall content of the email. If it seems too good to be true, it probably is. Scam emails may promise extravagant rewards, lottery winnings, or unexpected financial windfalls to lure recipients into taking action. Trustworthy organizations communicate in a professional and realistic manner. Emails that seem overly generous or make extraordinary claims without proper context should be treated with skepticism.
Check the Email Address Carefully:
Sometimes, cybercriminals use email addresses that look deceptively similar to legitimate ones. They may replace letters with similar-looking characters or add extra symbols to mimic official addresses. Take a close look at the sender’s email address, especially if the email is requesting sensitive information or financial transactions. Genuine emails from reputable sources will have accurate and correctly spelled email addresses.
Verify with Official Channels:

When in doubt, always verify the legitimacy of an email by reaching out to the company or individual through official channels. Use contact information obtained independently, such as from the company’s official website or customer service hotline. Avoid using contact details provided in the suspicious email itself, as these may lead to the scammers.
Conclusion:
In the digital landscape, recognizing the signs of a deceptive email is essential for protecting yourself from cyber threats. By staying vigilant and being aware of these five warning signs – unusual sender information, unexpected attachments or links, urgency and pressure tactics, grammar and spelling errors, and requests for personal information – you can enhance your email security and safeguard your personal and financial well-being. Remember, if an email seems too good to be true, it probably is.